The Back Story
E-Waste Management and Recycling are crucial for the protection of the environment and human health. The
improper disposal of electronic waste can lead to environmental pollution and health hazards. Renavart
Recyclers India
Private Limited has taken an opportunity to recover valuable materials, reduce waste, and conserve
natural resources. By
properly managing and recycling e-waste, we can promote sustainable development and protect the planet
for future
generations.
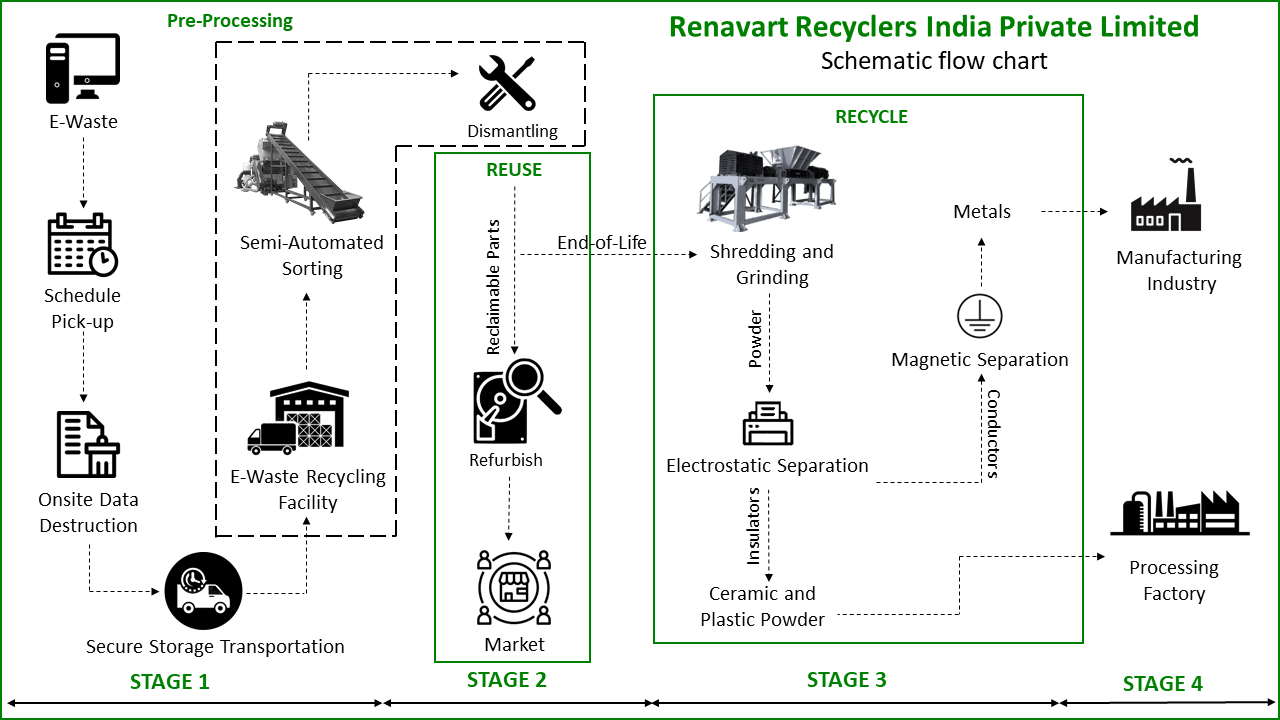
Stage 1: Collection, Storage and Logistics
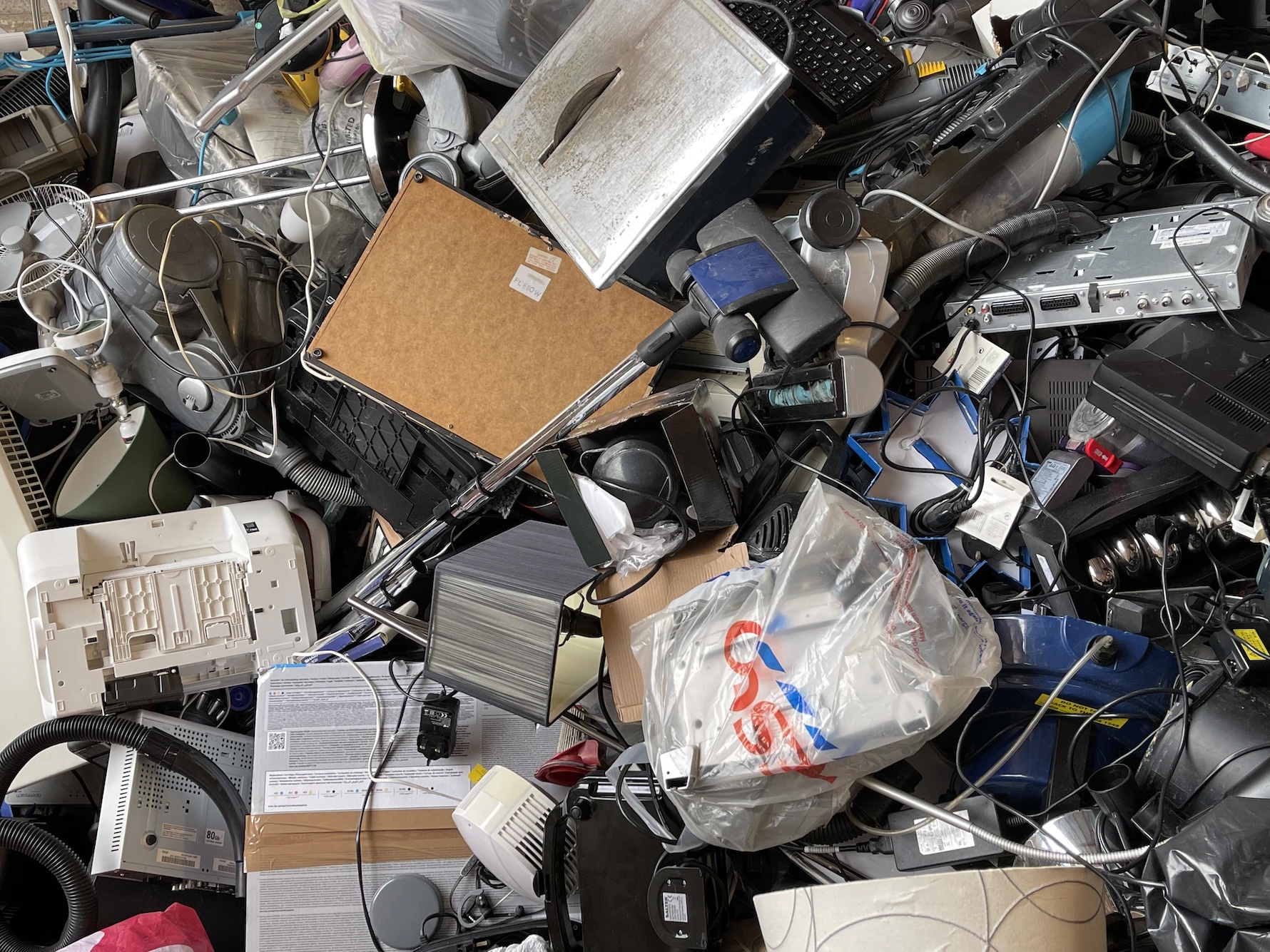
E-Waste procurement refers to the process of collecting and acquiring electronic waste for
recycling or disposal. This
can include items such as old computers, smartphones, televisions, IT equipment, and other electronic
devices that are no
longer in use.
Renavart Recyclers collects E-Waste from individuals, businesses, or government agencies, and may be done
through
various means, such as collection events, buy-back programs, or contracts with e-waste management companies.
However,
Renavart ensures that the materials are properly handled and disposed of in an environmentally responsible
manner.
One step quick and reliable solution to B2B and B2C through a business WhatsApp (Innovation)
(Type ‘Hi’, and get the solution at your fingertips)
E-Waste storage refers to the safe and secure containment of electronic waste, such as old
computers, televisions,
and other electronic devices, until they can be properly disposed of. This can include storing e-waste
in designated areas on
a temporary basis, or in specialized facilities designed for long-term storage and eventual recycling
or disposal.
Renavart Recyclers ensures the transport of or storing of E-Waste in the warehouse through
effective storage
technology such as heat-detecting cameras, fire extinguishers, humidity controlled, and monitoring in
order to protect the
environment and human health from harmful chemicals and materials that may be present in these devices.
Detailed safety
procedures and hazard control training will be ensured across all staff, including drivers, sorters,
warehouse, and office staff.
E-Waste logistics refers to the collection, transportation, and disposal of electronic waste.
This can include both the
logistics of collecting e-waste from households and businesses, as well as the logistics of transporting
it to a facility for
processing and disposal. E-waste logistics can also involve the management of the materials and
components recovered
from e-waste, such as precious metals, plastics, and glass. Effective e-waste logistics is important for
both environmental
and economic reasons, as it helps to keep harmful materials out of landfills and allows for the recovery
of valuable resources.
Stage 2: Sorting, Dismantling, and Refurbishing
E-waste segregation refers to the process of separating different types of electronic waste, such
as computers,
televisions, and mobile phones, into different categories based on their composition and
characteristics. This can include
separating different materials, such as plastics, metals, and glass, as well as different components,
such as circuit boards
and batteries. The segregation process is an important step in e-waste management because it allows for
the efficient and
effective recovery of valuable materials and components and can reduce the environmental impacts of
e-waste disposal.
Segregated e-waste is also easier to recycle, and for some materials, it's the only way to recycle it.
Renavart Recyclers ensures to note that e-waste segregation will be done by trained personnel and in
compliance
with the regulations and standards for e-waste management to avoid possible environmental and health
hazards. The
segregation processin the Renavart facility can be done through semi-automated technology, which can
improve the speed,
accuracy, and safety of the process, and help to achieve more efficient and sustainable e-waste
management.
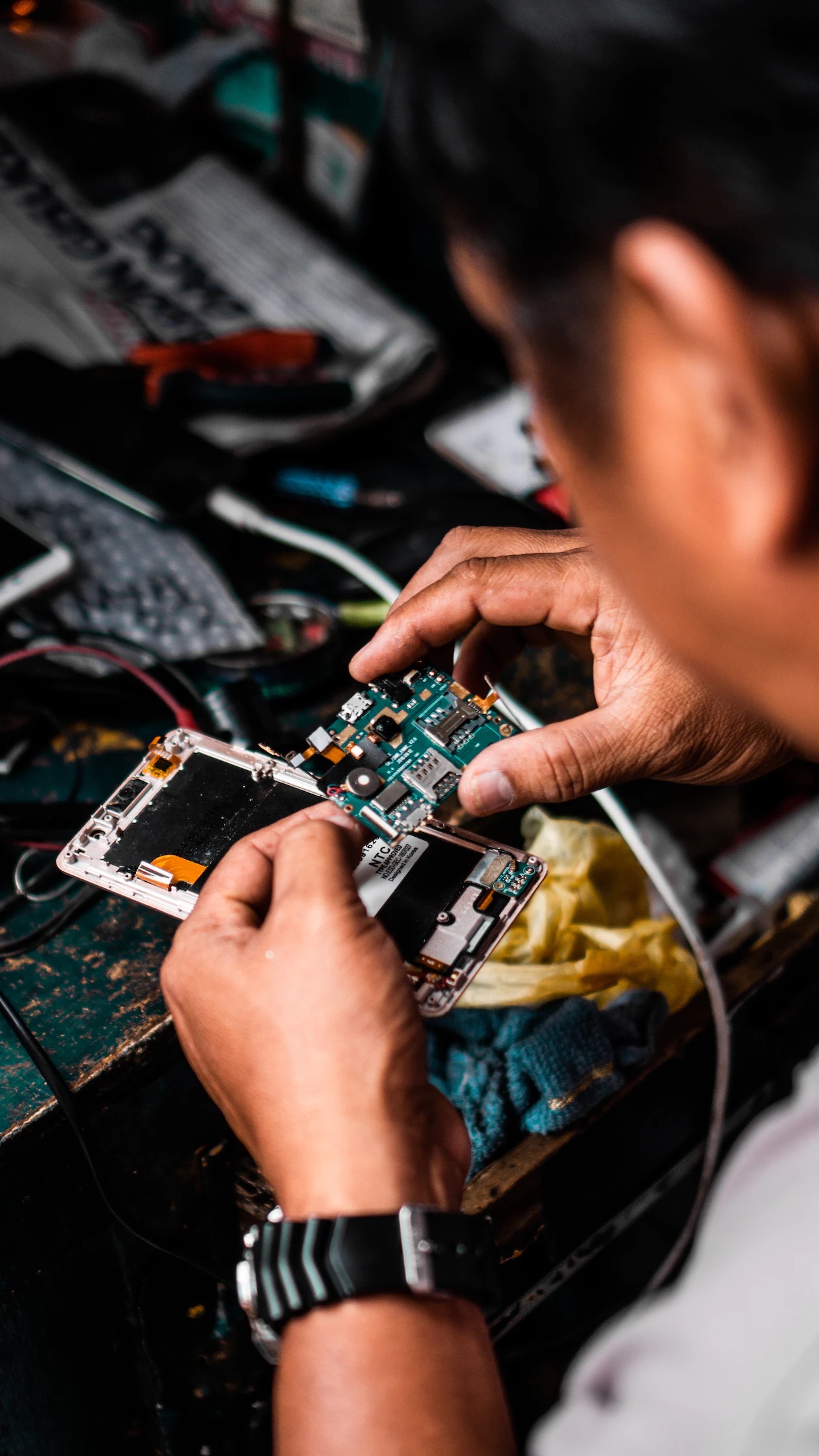
E-waste dismantling refers to the process of breaking down electronic devices in order to recycle
or dispose of their
components. Innovations in e-waste dismantling include the use of robotics and automation to improve
efficiency and
safety.
Refurbishing e-waste is a process of repairing or upgrading electronic devices that are no longer
in use, with the aim
of giving them a new life. This process involves cleaning, repairing, and upgrading the devices to
extend their lifespan and
reduce electronic waste. During the refurbishing process, any faulty parts are replaced, and the devices
are tested to ensure
they function properly. Once the refurbishing is complete, the devices can be sold, donated, or given
away for reuse, which
helps to reduce electronic waste and conserve natural resources.
Renavart Recyclers seeks that Refurbishing e-waste is an important step in promoting sustainable
development and
reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste. By giving used electronics a new life, we can
help to reduce the
amount of e-waste that ends up in landfills, which in turn helps to reduce pollution and negative impact
on the environment.

Stage 3: Shredding and Processing
Shredding and mechanical processing are important steps in e-waste recycling that involve breaking down
electronic
devices into small particles to facilitate the separation of valuable metals from non-metallic
components. Shredding involves
using high-powered machines to break down electronic devices into small pieces, which are then sorted
based on their type
and composition. The shredded material is then passed through a series of mechanical processes such as
screening, sorting,
and grinding to further separate the valuable metals from the non-metallic components
The mechanical processes used to recover the metals from the shredded e-waste include air separation,
magnetic
separation, and eddy current separation. Air separation uses air currents to separate the lighter
non-metallic components
from the heavier metal particles. Magnetic separation is used to separate magnetic materials such as
iron and steel from
non-magnetic components. Eddy current separation uses high-frequency magnetic fields to separate
conductive metals
such as copper and aluminum from non-conductive materials.
Stage 4: Recovered Materials to Manufactures
The valuable metals are recovered from E-Waste recycling. Furthe, they can be sold to manufacturers who
use them to
produce new electronic devices and other products. By recovering these metals from e-waste, we can
conserve natural
resources and reduce the environmental impact of mining and processing raw materials.
Environmental Impact
E-waste recycling has significant environmental benefits, including the reduction of greenhouse gas
emissions, energy
savings, and conservation of natural resources. Recycling electronic devices reduces the need for new
raw materials, which
conserves natural resources and reduces the energy required to produce new devices.
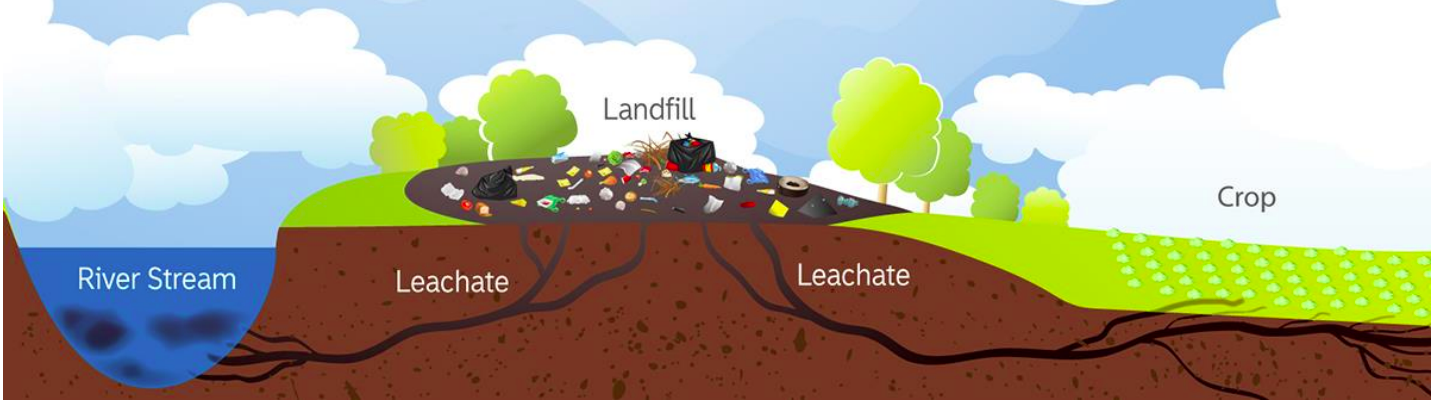
In addition, e-waste recycling helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by diverting electronic waste
from landfills,
which produce harmful methane gas. Landfills also contribute to soil and water pollution, which can have
negative effects
on human health and the environment. Recycling electronic devices also helps to save energy by reducing
the need for
energy-intensive mining and processing of raw materials. By recovering valuable metals from e-waste, we
can reduce the
environmental impact of mining and processing while conserving natural resources
Benefits of E-Waste Recycling
In India, E-Waste management and recycling have become increasingly important in recent years due to the
rapid
growth in the use of electronic devices and the resulting increase in electronic waste. Effective
e-waste management and
recycling practices have numerous benefits, including:
E-waste contains hazardous materials that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. When electronic waste is not recycled or disposed of correctly, it can pollute water, air, and soil, which can lead to serious environmental problems. By properly managing and recycling e-waste, we can reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste and protect the environment for future generations.
E-waste contains hazardous materials that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. When electronic waste is not recycled or disposed of correctly, it can pollute water, air, and soil, which can lead to serious environmental problems. By properly managing and recycling e-waste, we can reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste and protect the environment for future generations.
E-waste contains valuable materials, such as gold, silver, copper, and other metals that can be recycled and reused. By recycling e-waste, we can conserve these resources and reduce the need to extract new materials from the earth, which can lead to the depletion of natural resources.
E-waste management and recycling can also have economic benefits. By recovering valuable materials from electronic waste, we can create new jobs and industries in the recycling sector. This can also help reduce the cost of raw materials for manufacturing, making products more affordable and accessible for consumers.